IMPORTANCE OF WATER
Water is one of the main constituents on earth. More than two thirds of the earth is covered by water.
Approximately 70 percent of the any organism is formed of water. Water is the most abundant
component in any organism, the lowest is 20% in seeds and bones and highest is 85-90% in brain cells.
Jellyfish has exceptionally large amount of water i.e., 99% (hence the body shows transparency).
Properties of water :
The properties of water that make it the cradle of life are:
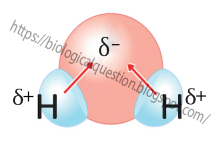
1. High Polarity
The bonds which are formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms are called covalent
bonds. Normally the sharing of electrons between two atoms is fairly equal and the covalent bond is
nonpolar. In the case of water, however the sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen is not
completely equal so the covalent bond is polar. A polar covalent bond is a chemical bond in which shared
electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it partially negative and the other
atom partially positive. Thus, in H2O, the O atom actually has a slight negative charge and each H atom
has a slight positive charge, even though H2O as a whole is neutral. Because of its polar covalent bonds,
water is a polar molecule i.e., it has a slightly negative pole and two slightly positive ones.
This is polarity of water molecules that makes it an excellent or universal solvent for polar substances.
Ionic compound or electrolytes can be easily dissolved in water, non-polar substances having charged
groups in their molecules can also be dissolved in water. Such compounds when dissolved in water,
disassociates into positive and negative ions and are in more favourable state to react with other
molecules and ions. This is the reason why all chemical reactions in living beings occur in aqueous
medium.
Polarity of water Molecule
2. Hydrogen Bonding:
The polarity of water molecules makes them interact with each other. The charged regions on each
molecule are attracted to oppositely charged regions on neighbouring molecules, forming weak bonds.
Since the positively charged region in this special type of bond is always an H atom, the bond is called a
hydrogen bond. This bond is often represented by a dotted line because a hydrogen bond is easily
broken.
Because of hydrogen bonding, water is a liquid at temperatures suitable for life. The high cohesion and
adhesion force of water is due to the presence of hydrogen bonds in water, which in turns makes water
as transport medium.
Hydrogen Bond between water Molecule
3. Cohesion and Adhesion:
Cohesion is the attraction among the water molecules which enables the water molecules to stick
together. Water flows freely due to cohesion. Water molecules also have attraction to polar surfaces.
This attraction is called adhesion. Both cohesion and adhesion are due to hydrogen bonds among water
molecules. These properties of water enable it to circulate in living bodies and to act as transport
medium.
4. High specific heat capacity:
Heat capacity can be defined as the amount of heat required for minimum increase in temperature of a
substance. The specific heat capacity of water can be represented as number of calories required to raise
the temperature of 1g of water up to 1oC i.e., 1 Calorie (4.18 Joules). Water has relatively a very high
heat capacity than any other substance due to its hydrogen bonding, because much of the heat
absorbed by water is utilized in the breakdown of hydrogen bonding therefore it does not manifest itself
to raise the temperature of water. Hence, very large amount of heat can increase very little in
temperature in water. Due to its high heat capacity water works as temperature stabilizer or regulator for
organisms in the hot environment and hence protects the living material against sudden thermal
changes.
5. High heat of vapourization:
Heat of vapourization is the amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of a liquid into gaseous
form. Heat of vapourization of water is represented as number of calories absorbed per gram
vapourized. Water has high heat of vapourization i.e., 574 calories per gram. The high heat of
vapourization means that a large amount of heat can be lost with minimal loss of water from the body.
This is high heat of vapourization of water that gives animals an efficient way to release excess body heat
in a hot environment. When an animalsweat, body heat is used to vapourize the sweat thus cooling the
animal. Due to this property of water, evaporation of only 2ml out of one litter of water lowers the
temperature of the remaining 998 ml water by 1 C.
6. Hydrophobic exclusion :
Hydrophobic exclusion can be defined as reduction of the contact area between water and hydrophobic
substances which are placed in water. For example, if you place few drops of oil on the surface of a water
solution, the oil drops will tend to join into a single drop. Biologically, hydrophobic exclusion plays key
roles in maintaining the integrity of lipid bilayer membranes.
Hydrophobic exclusion
7. Ionization :
The dissociation of a molecule into ions is called ionization. When water molecule ionizes, it releases an
equal number of positive hydrogen and negative hydroxyl ions.
This reaction is reversible but equilibrium is maintained at 25°C. The H* and OH ions affect and take part
in many of the reactions that occur in cells, e.g., it helps to maintain or change the pH of the medium.
Ionization of water
8. Lower density of ice :
Ice floats on water. This is because ice is less dense than water. The reason is that ice has a giant
structure and show maximum number of hydrogen bonding among water molecules; hence, they are
arranged like a lattice. In freezing weather, ice forms on the surface of ponds and lakes forming an
insulating layer above the water below. This provides a living environment for some organisms until the
ice melts. Organisms can also live under the ice.
Lattice likes arrangement of water molecule in ice
Thank you Reading the article.






.png)


0 Comments